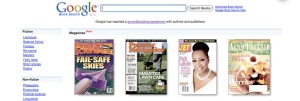
“A Photo Editor” blogger Rob Haggart reports that Rodale, which is a magazine publisher, is publishing back issues of the magazine on Google. They are available through Google Book Search. Here is a post about it on Google as well.
Haggart brings up the amusing point of what to do with magazines that basically write the same articles every month.
But he also brings up the question of whether the magazine is violating copyright a/la New York Times v. Tasini, which ruled that publishers did not have a right to relicense content to database without the contributor’s consent. (If in fact this is an arrangement between the publishers and google, and not an independent act by google)
My opinion (as a student of the law, not as a judge or lawyer) is that this is permissible, based on the Tasini opinion, which by coincidence, we read last week in my copyright course.
The big difference between Google magazines and Tasini is that Tasini involved a large database where the articles could appear along with completely unrelated articles or alone. They didn’t appear in context, and so they didn’t qualify as permissible revisions.
In the current situation, the articles and photographs appear in context and I think they would be considered permissible revisions. Which is not to say that Google can post them without the magazine’s consent, but only that the magazines can authorize Google to post them without the photographer’s consent.
From Tasini:
“A newspaper or magazine publisher is thus privileged to reproduce or distribute an article contributed by a freelance author, absent a contract otherwise providing, only “as part of” any (or all) of three categories of collective works:
(a) “that collective work” to which the author contributed her work,
(b) “any revision of that collective work,” or
(c) “any later collective work in the same series.”
In accord with Congress’ prescription, a “publishing company could reprint a contribution from one issue in a later issue of its magazine, and could reprint an article from a 1980 edition of an encyclopedia in a 1990 revision of it; the publisher could not revise the contribution itself or include it in a new anthology or an entirely different magazine or other collective work.” H. R. Rep. 122-123″
I think if a photographer took this case to court, it would look more like Greenberg v. National Geographic. In that case, a court ruled in favor of the publisher’s right to republish a digital “revision” of the magazine without permission of the photographer. The magazine pages on the CD ROMs in the NGS case were presented in their original context, whereas the Tasini articles in the Lexis and other databases were not. Seems like a small difference, but it makes all the difference.
A good way to distinguish the two is to think about the good old microfilm days. If it looks like microfilm (you have to look at the entire page in context) then it is more like the Greenberg case. The Google Magazine search looks more like microfilm.
Keep in mind that each case has the potential to be different based on the facts, and a contractual agreement between a magazine and a photographer may change the equation. Also, if this is not an arrangement with the publishers, but is instead google going out on it’s own, it is a different kind of trouble.
Ironically, this google magazine search could be a major blow to Lexis Nexis. Why pay LN fees to search magazines when you can do it for free on Google.
Reminder: this should not be considered legal advice. See disclaimer.
Ah, yes. In my opinion, the Greenberg case is a setback for all freelancers. It allows reuse of a work in a fashion (technically, by the courts not a new use) in a way not envisioned when any original agreement was made between the publisher and the artist.
And with the publishing industry in the tank, it offers a new source of revenue without the annoying problem of additional compensation for its contributors. Photographers will, of course, continue to suffer new erosion of copyright as the push for “Orphan Works”, the convoluted interpretation of “fair use” and “transformative works” are used by the intellectually bankrupt and creatively challenged individuals and companies.
Leif Skoogfors